Description
Overview
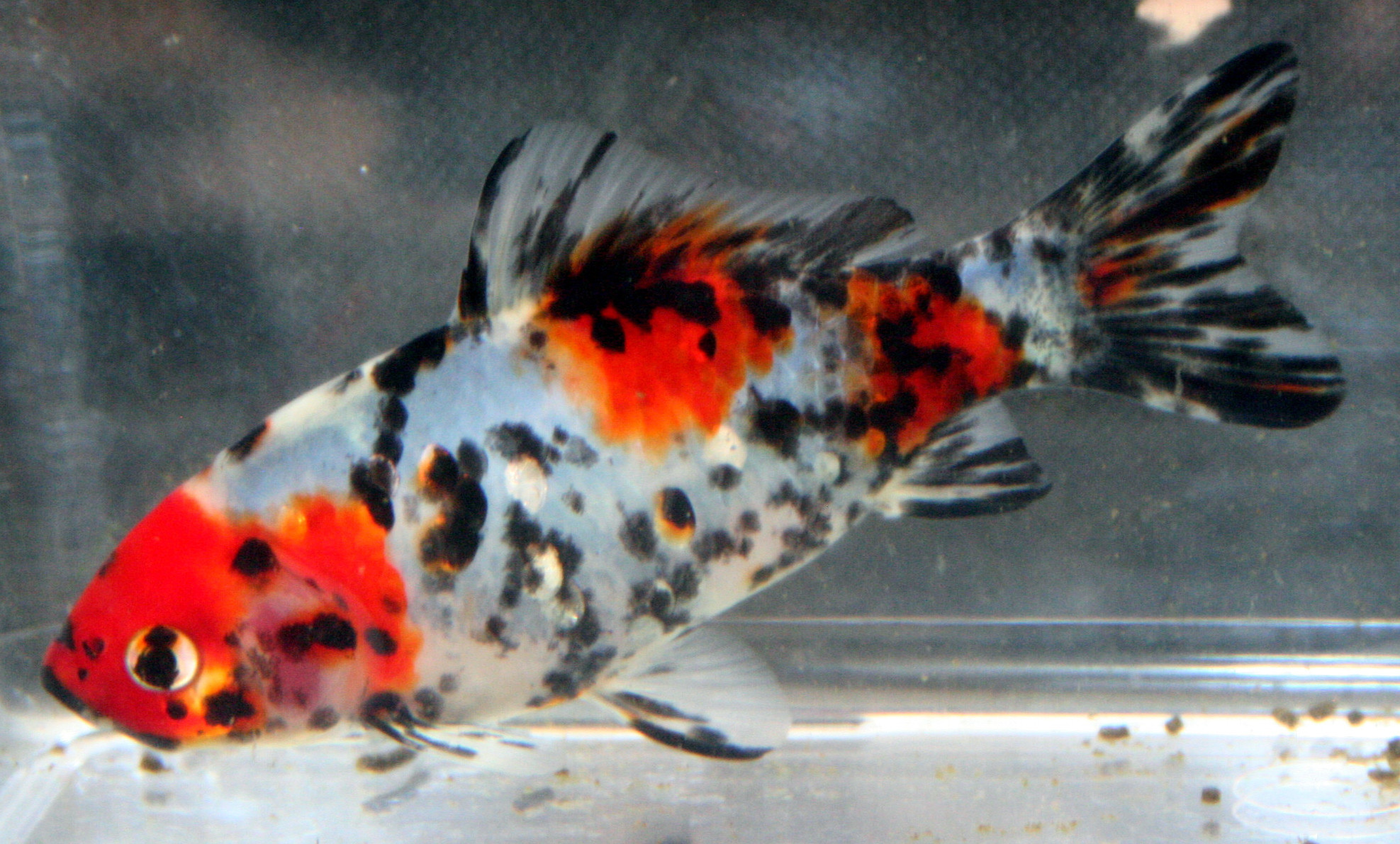
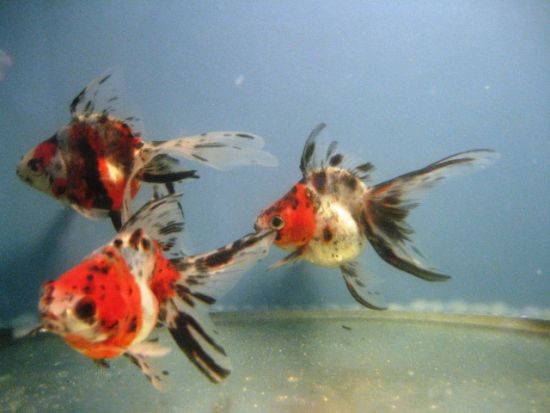
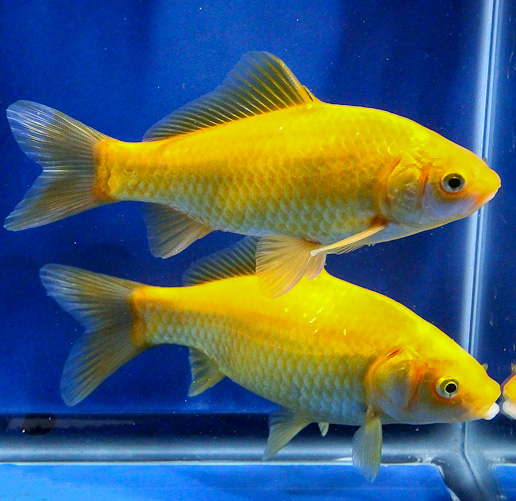
It has an elongated and flat body with short and broadly triangular naked head. In wild populations, body color varies from fish to fish such as olive brown, slate olive, olive green with a bronze sheen, silvery, grayish yellowish, gray-silver, gold to creamy white often with black blotches, yellowish white, white below or even creamy white while cultured forms vary through scarlet, red-pink, silver, brown, white, black and combinations of these colors. It has a long dorsal fin with 15 to 21 soft rays with slightly concave edge. A hard serrate spine is seen at the origin of the dorsal and anal fins. Anal fin contains 2-3 spines and 4-7 soft rays while pelvic fin is short, broad and thoracic. Caudal fin is forked with 17-19 soft rays. Barbels are absent on the upper jaw while lateral line is complete with 27-31 scales. Three types of Shubunkin are recognized on the basis of finnage such as the Japanese or American Shubunkin, the London Shubunkin and the Bristol Shubunkin. The Japanese or American Shubunkin has deeply forked caudal fins that end in long narrow lobes while the caudal fins of London Shubunkins have rounded lobes with very minimal forking and the Bristol type Shubunkin has a massive caudal fin that is very wide, moderately forked with well-rounded lobes. It is omnivorous and in wild it mainly feeds on plants, detritus, small crustaceans and insects. The shubunkin goldfish reaches sexually mature at 2 to 3 years of age. It can grow up to 30 cm in length and can live up to 25 years or more with proper care.
Feeding
It is omnivorous and in wild it mainly feeds on plants, detritus, small crustaceans and insects. In captive condition it accepts all kinds of fresh, frozen and flake foods. It also takes frozen plankton, Daphnia, beef heart, brine shrimp, glass worms and blood worms, vegetable diet such as fresh spinach, zucchini, peas and lettuce etc. To keep your fish healthy, give them a high quality flake food every day. Feed should be offered 2-3 times a day.
Housing
Shubunkin Goldfish is the more popular fish among the aquarium fish keeper. It is extremely fast and agile swimmer which requires at least 15 gallons tank with lots of space for swimming. The tank should have smooth rocks or driftwood with some live plants which helps to create a natural and comfortable environment for your fish. The tank should also have good water chemistry with a pH of 6.0-8.0 and hardness of 5 – 19 dGH. It is a cold water fish which does best at temperature between 65 and 72° F. Shubunkins are ravenous eaters and produce a significant amount of waste. For this reason, adequate filtration is required for the shubunkin aquarium. Partial water changes weekly or every other week are strongly recommended which helps to keep your fish healthy and provide for a cleaner, nicer-looking tank. Snails can also be added as they reduce the algae in the tank and it helps to keep the tank clean. They are very social, peaceful and schooling fish which should be kept with other Pond Comets, Koi, Butterfly Koi and other gold fishes. It should not be kept with slower-swimming tank mates.
Breeding
The shubunkin goldfish is an egg layer which can easily breed in captive condition. In wild condition it breeds during the summer. Spawning takes place in shallow water among weeds where willow roots grow. Spawning activity begins just before dawn to mid-afternoon. Breeding occurs year-round in captivity under the right conditions. The breeding tank should have a flourishing environment with solid surfaces for the eggs. In this case bushy, oxygenating plants such as Anacharis or artificial plants or fibrous spawning mops can also be used. They spawn when the temperature is between 68° and 74° F. Before spawning, parents should be conditioned with high protein food such as live brine shrimp and worms. To maintain the breeding tank partial water changes of up to about 20% per day is recommended. During the spawning, the mature female lays sticky eggs which are attached to the aquatic plants or spawn mop. Spawning lasts about two or three hours and the single female can produce up to 10,000 eggs. After spawning the parents should be removed from the tank to prevent eating the eggs. The fertilized eggs hatch in 4 to 7 days and the newly hatched dark brown or black colored fry should be fed with goldfish specialty fry foods until they become big enough to eat flake or brine shrimp. They reach sexual maturity at 2 to 3 years of age and it depends on water temperature and other aspects of water quality.
Sexing
It is difficult to make differences between the male and female shubunkin. Generally the male is smaller and more slender than the female. During the breeding season the male has white prickles (breeding tubercles) which are seen on its operculum and head. The anal fin of the male is concave whereas on the female it is convex. The breeding female has a fatter appearance when it is viewed from the above.
Availability
The Shubunkin Goldfish is very beautiful fish due to their always speckled or a variegated color pattern. It is very hardy and it can be kept in aquarium with any conditions. It is readily available in fish stores and online vendor with reasonable price.
Written specially and exclusively for koi on demand by Dr. A.K.M. Nazrul Kabir









Reviews
There are no reviews yet.